Projects
Miramar Pure Water
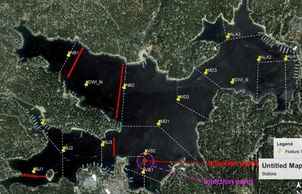
Otay & Miramar Tracer Study
Otay & Miramar Tracer Study

WQS provided technical support to the City of San Diego in assessing the water quality effects of augmenting Miramar Reservoir with highly treated purified water. WQS developed a 3D water quality model (AEM3D, successor to ELCOM/CAEDYM model) and helped design tracer studies to validate the model. This project has received regulatory approval and is under construction.
Otay & Miramar Tracer Study
Otay & Miramar Tracer Study
Otay & Miramar Tracer Study

WQS provided technical support to the City of San Diego for design and execution of a tracer study in Otay and Miramar Reservoirs. This work identified an injection site, a data collection plan, and the time-frame for a hydrodynamic tracer study. The tracer study validated our 3D hydrodynamic models, as required by DDW Pure Water regulations. Model validation was verified by an independent advisory panel.
Lake Casitas HOS
Otay & Miramar Tracer Study
Lake Champlain 3D Modeling

This investigation evaluated the viability of various hypolimnetic oxygenation systems (HOS) in the lake for Casitas Municipal Water District. Three oxygenation systems were evaluated: Speece Cone, Diffused Oxygenation, and an SDOX® system. Diffused Oxygenation was identified as the best alternative due to favorable costs and ease of implementation. The project was constructed in 2015 and has been operating successfully since installation.
Lake Champlain 3D Modeling
Lake Champlain 3D Modeling
Lake Champlain 3D Modeling

Water Quality Solutions developed a 3D hydrodynamic and water quality model of the Inland Sea of Lake Champlain, including Missisquoi Bay and St. Alban’s Bay. This model captures the spatial and temporal extent of cyanobacteria harmful algal blooms (HABs) in the shallow bays. The model will be used to simulate the effects of changing climate and land use on water quality in the eastern bays of Lake Champlain in collaboration with University of Vermont.
San Vicente Pumped Storage
Lake Champlain 3D Modeling
San Vicente Pumped Storage

WQS completed a project for the City of San Diego to assess the effects of Pumped Storage (PS) operation on the water quality in San Vicente Reservoir under different operating scenarios. A 3D reservoir model was used to predict the effects of pumped storage on reservoir mixing and water quality. The model shows water quality is maintained under a range of pumped storage operating conditions.
Scottsdale Reservoir Inlet
Lake Champlain 3D Modeling
San Vicente Pumped Storage

WQS performed Computational Fluid Dyamics (CFD) modeling using Fluent® for Waterworks Engineers on behalf of the City of Scottsdale to address reservoir mixing. This study evaluated potential modifications to the inlet/outlet design to improve water mixing, and identified an optimal inlet design for the reservoir.
Lake Casitas Water Quality
Sweetwater Reservoir Aeration
Sweetwater Reservoir Aeration

WQS has performed detailed water quality data analysis on Lake Casitas since 2012. WQS also recommended an optimized data sampling plan, which was implemented by Casitas Municipal Water District. WQS recently analyzed the effects of the Thomas Fire on water quality in the lake and its watershed, exploring the effects of fire on disinfection by-product levels in the water distribution system.
Sweetwater Reservoir Aeration
Sweetwater Reservoir Aeration
Sweetwater Reservoir Aeration

Sweetwater Reservoir has experienced harmful algal blooms (HABs) and high manganese levels due to high external nutrient loading and low dissolved oxygen levels resulting from the decay of organic matter. WQS evaluated several potential water quality improvement strategies: hypolimnetic oxygenation, destratification, and vigorous mixing. We identified destratification using a compressed air diffuser as the preferred option, and employed DYRESM modeling to size and optimize the air diffuser design.
San Vicente Pure Water
Sweetwater Reservoir Aeration
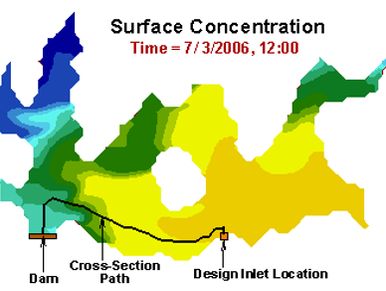
WQS completed a project for the City of San Diego to assess the effects of augmenting the reservoir by adding highly treated purified water. WQS performed a detailed water quality analysis and supported implementation of a data sampling plan. This project received concept approval from the California Division of Drinking Water and is being considered as the location for Phase II of San Diego Pure Water.
Lake Arrowhead IPR
WQS’s Imad Hannoun acted as subject matter expert in producing a “best practices guidance manual” for performing tracer studies and validating hydrodynamic models for indirect potable reuse (IPR). The project was funded by US Bureau of Reclamation and included a full-scale tracer study. The resulting manual will be available via the US Bureau of Reclamation.
Lake George State of the Lake
Imad Hannoun, President of WQS, served as a science advisor to The Fund For Lake George and co-author of the Lake George State of the Lake Report, which outlines threats from invasive species, rising salt levels, and declining water quality and clarity. This study examined changes to the lake over a 30-year period and identified strategies for future lake management such as curbing major nutrient and contaminant sources.
Salt Lake City Clarifiers
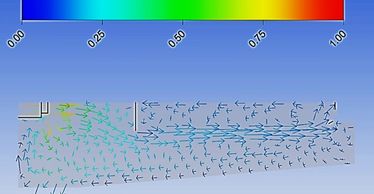
WQS performed Computational Fluid Dyamics (CFD) modeling using Fluent® for Waterworks Engineers on behalf of Salt Lake City Public Utilities. The modeling addressed various aspects of sludge settling and evaluated potential design modifications. This modeling identified the best clarifier design for the client.
Hodges Reservoir HOS

WQS developed a three-dimensional water quality model of the reservoir using AEM3D for the City of San Diego and the San Diego County Water Authority. Hodges Reservoir experienced low dissolved oxygen from decaying organic matter, as well as harmful blue-green algal blooms (HABs). The model evaluated the benefits of a hypolimnetic oxygenation system (HOS) and assessed the impacts of watershed nutrient reduction and mixing on water quality, including algal productivity and dissolved oxygen. These results assisted evaluating the benefits of a Speece Cone HOS. The Speece Cone was successfully installed in 2020.
Diamond Valley Lake

WQS provided technical support to the Metropolitan Water District of Southern California in analyzing water quality data including dissolved oxygen, chlorophyll a, zooplankton, and algal composition in Diamond Valley Lake. Recommendations were provided regarding future lake operations and water quality monitoring.



Copyright © 2021 Water Quality Solutions Inc - All Rights Reserved.